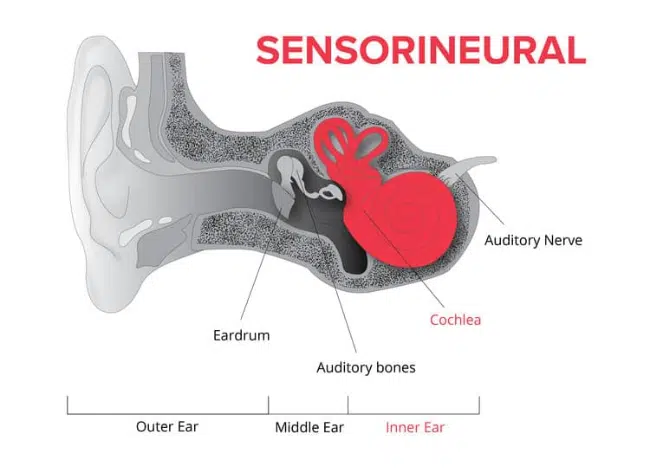
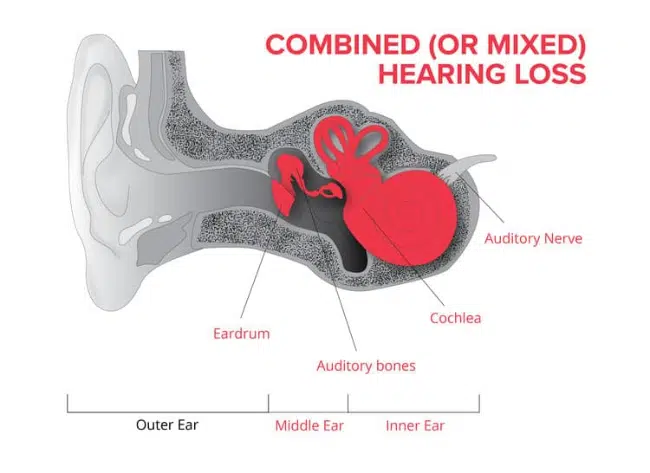
Sometimes a conductive hearing loss occurs in combination with a sensorineural hearing loss(SNHL). In other words, there may be damage in the outer or middle ear and in the inner ear(cochlea) or auditory nerve. When this occurs, the hearing loss is referred to as a mixed hearing loss.